Introduction
India, with its rich history spanning millennia, has been a cradle of knowledge, science, and technology since ancient times. From the sophisticated urban planning of the Indus Valley Civilization to the development of early mathematics and astronomy, India’s contributions have left an indelible mark on global intellectual heritage. This essay explores the evolution and impact of knowledge, science, and technology in India through different historical periods, highlighting key advancements, notable figures, and their contemporary relevance.
Ancient India: Foundations of Knowledge and Science
#### Indus Valley Civilization (c. 3300–1300 BCE)
The Indus Valley Civilization, one of the world’s oldest urban societies, flourished in present-day Pakistan and northwest India. Known for its well-planned cities like Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, civilization demonstrated advanced knowledge in urban planning, drainage systems, and brick-making techniques. The seals discovered from this era suggest a writing system that remains undeciphered, hinting at an early form of written communication.


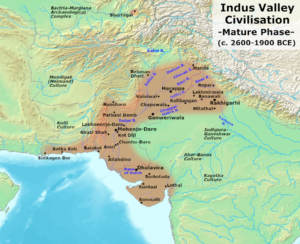
The city layout of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, with their grid-like streets, advanced sanitation systems, and public baths, indicates a sophisticated understanding of urban planning and public health. The Great Bath of Mohenjo-daro, constructed with finely fitted bricks and equipped with a sophisticated drainage system, reflects the civilization’s engineering prowess and civic planning.
#### Vedic Period (c. 1500–500 BCE)
The Vedic period saw the composition of the Vedas—ancient texts revered as foundational scriptures of Hinduism. These texts encompassed a wide range of knowledge, including hymns, rituals, philosophy, and early astronomy. The Vedas contain references to celestial bodies, seasons, and agricultural practices, indicating a keen observation of natural phenomena and their integration into religious ### Mathematics and Astronomy: Aryabhata and Brahmagupta
India made significant contributions to mathematics and astronomy during this period. Aryabhata (476–550 CE), a brilliant mathematician and astronomer, developed the concept of zero, the decimal system, and calculated the value of π (pi) accurately. Brahmagupta (598–668 CE) further advanced mathematical knowledge with his work on algebra and solutions to quadratic equations. Their contributions laid the foundation for later developments in mathematics and had a profound influence on global scientific thought.

### Medieval India: Synthesis and Advancement
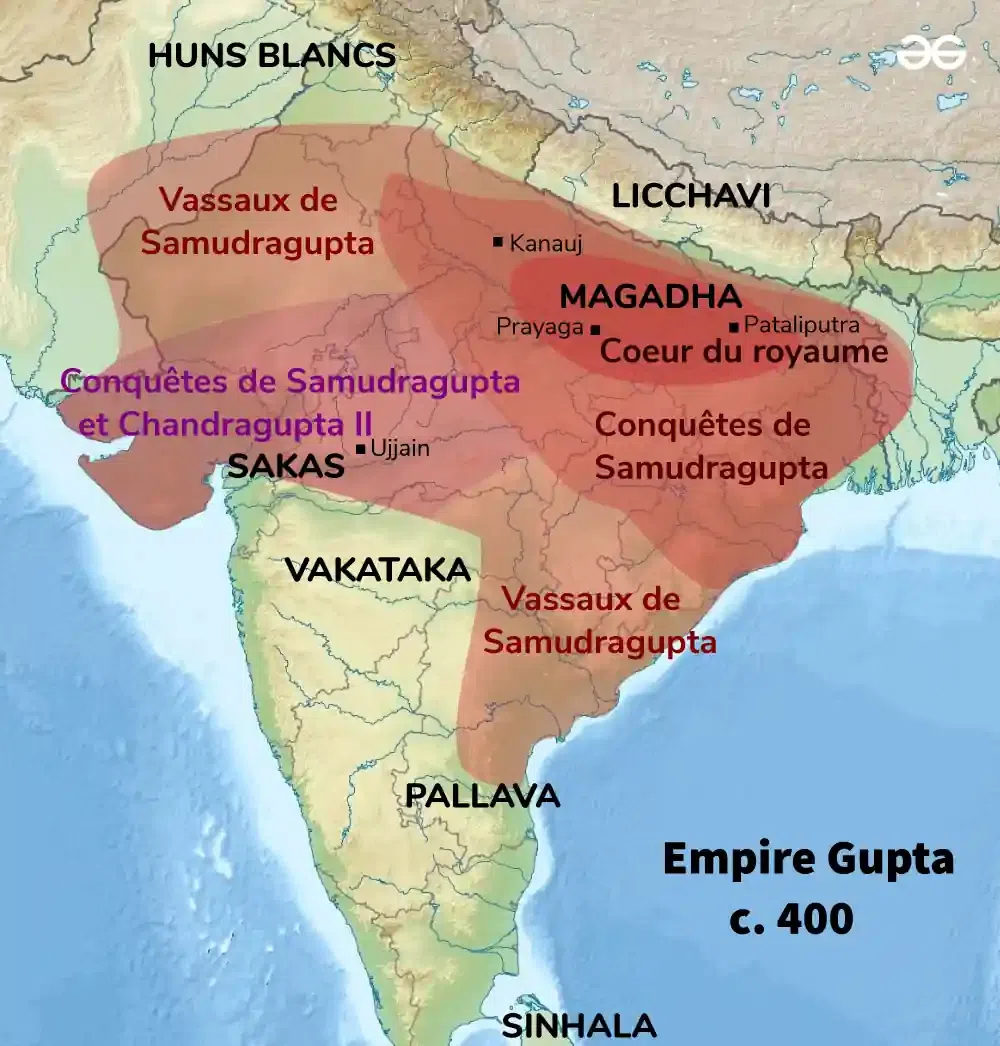
#### Gupta Empire (c. 320–550 CE)
The Gupta period is often referred to as the Golden Age of India, marked by flourishing art, literature, and scientific achievements. Scholars like Varahamihira made significant contributions to astronomy, while Aryabhata’s works were further developed and disseminated. The Nalanda and Takshashila universities emerged as centers of learning, attracting students and scholars from across Asia.
#### Medicine and Surgery: Sushruta and Charaka
Sushruta (c. 6th century BCE), known as the father of surgery, authored the Sushruta Samhita, a seminal text on surgery and medicine. His pioneering techniques in plastic surgery, cataract surgery, and the use of surgical instruments showcased India’s advanced medical knowledge. Charaka (c. 300 BCE) compiled the Charaka Samhita, a comprehensive treatise on Ayurveda that outlined principles of diagnosis, treatment, and herbal medicine.
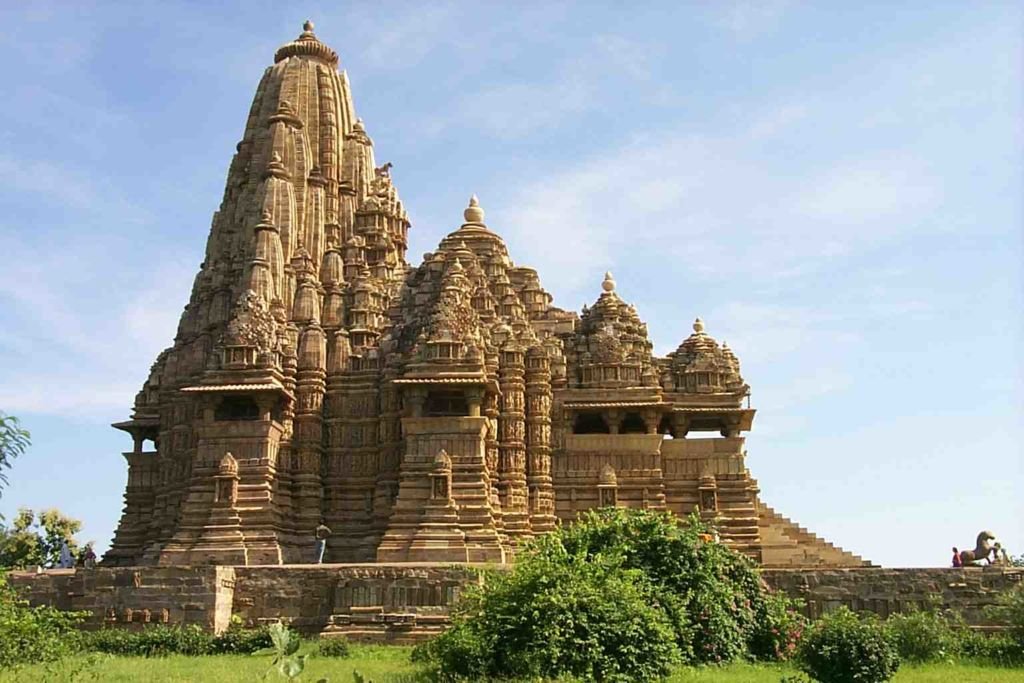
#### Architecture and Engineering: Temple Construction
The medieval period witnessed remarkable advancements in architecture and engineering, particularly in temple construction. The temples of Khajuraho, Ellora, and Konark exemplify intricate craftsmanship, innovative structural design, and artistic expression. These monuments stand as enduring symbols of India’s architectural prowess and cultural heritage.

### Colonial Era: Encounter and Transformation
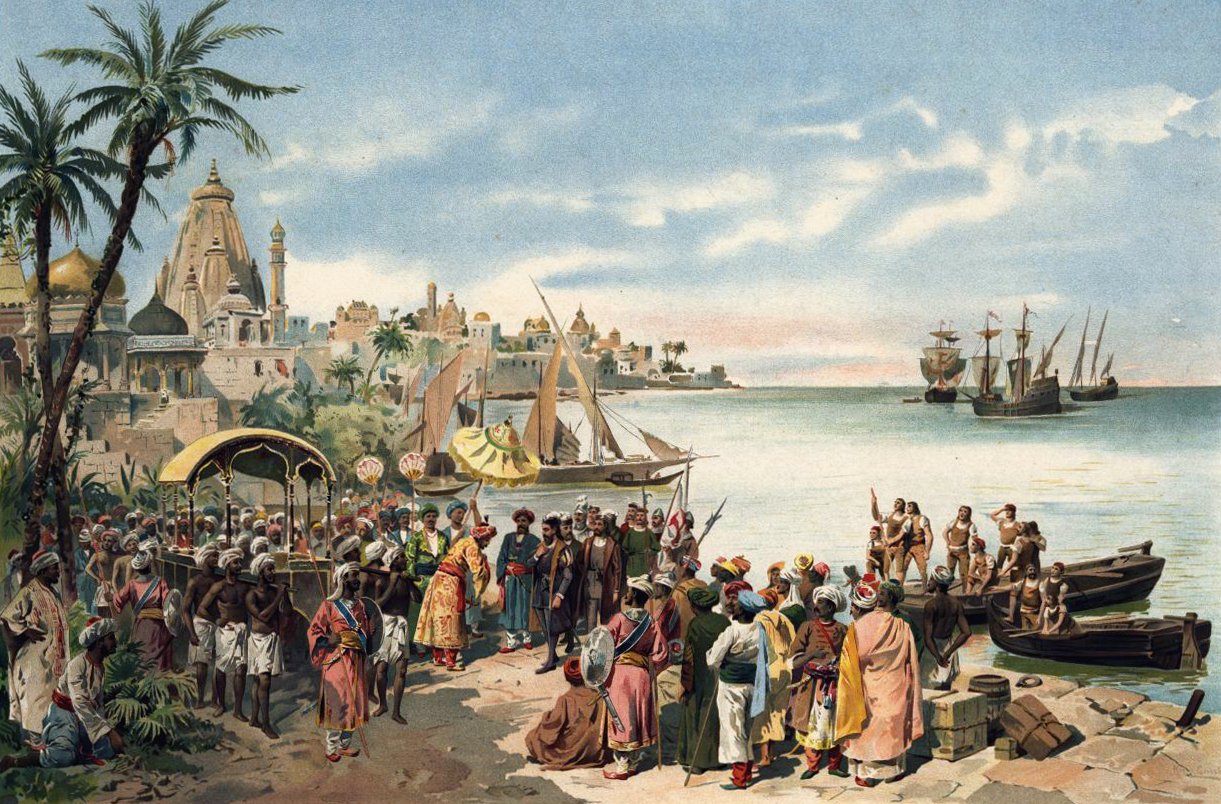
#### Impact of European Encounters
The arrival of European powers in the 15th century marked a significant turning point in India’s scientific and technological landscape. While the British East India Company initially focused on trade, subsequent colonization led to the establishment of institutions like the Calcutta Mathematical Society and the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science. These institutions facilitated the exchange of scientific ideas and promoted education in modern scientific disciplines.

#### Indian Renaissance: Raja Ram Mohan Roy and Scientific Rationalism
The 19th century witnessed a cultural and intellectual renaissance in India, often referred to as the Bengal Renaissance. Figures like Raja Ram Mohan Roy advocated for social reforms, women’s rights, and the promotion of scientific education. The establishment of institutions like the Asiatic Society and the Indian Association fostered scientific inquiry and contributed to the dissemination of knowledge across various disciplines.
### Modern India: Independence and Technological Advancement
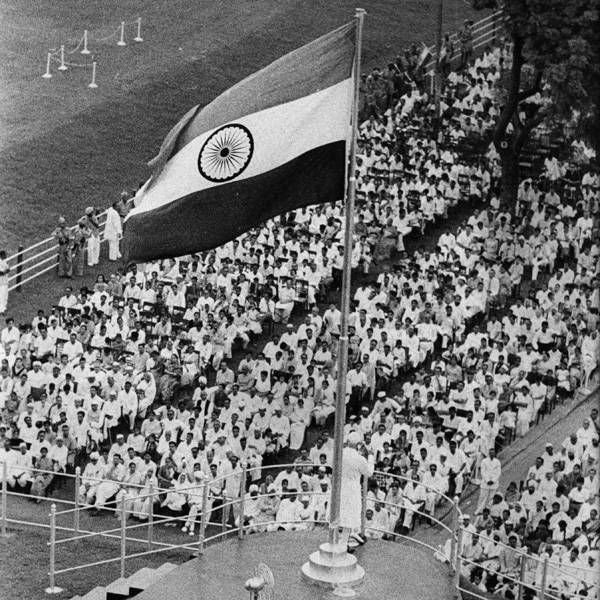
#### Post-Independence Scientific Institutions
India’s independence in 1947 marked a new phase of scientific and technological development. The establishment of institutions like the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) played a pivotal role in promoting research, innovation, and technological self-reliance. ISRO’s successful space missions, including the Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), showcased India’s capability in space exploration and satellite technology.

#### Information Technology Revolution
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed the rapid growth of India’s information technology (IT) sector. Cities like Bangalore emerged as global IT hubs, attracting multinational corporations and fostering innovation in software development, telecommunications, and digital services. The success of Indian IT professionals globally underscored India’s potential as a leader in the knowledge economy.
### Contemporary Challenges and Future Prospects
#### Challenges in Education and Research
Despite significant advancements, India faces challenges in ensuring equitable access to quality education and research opportunities. Disparities in infrastructure, funding constraints, and curriculum reforms remain areas of concern. Addressing these challenges is crucial for nurturing the next generation of scientists, engineers, and innovators.
#### Embracing Innovation and Sustainability
In an increasingly interconnected world, India has the opportunity to leverage its strengths in science and technology to address global challenges such as climate change, healthcare, and sustainable development. Initiatives like the Atal Innovation Mission and Swachh Bharat Abhiyan exemplify India’s commitment to fostering innovation and promoting sustainable practices.

### Conclusion
India’s journey in knowledge, science, and technology spans millennia, characterized by a rich tapestry of achievements, innovations, and intellectual contributions. From ancient mathematical treatises and surgical techniques to contemporary advancements in space exploration and IT, India continues to play a pivotal role in shaping global scientific discourse. As India navigates the complexities of the 21st century, harnessing its intellectual capital and promoting scientific inquiry will be crucial in addressing global challenges and advancing human progress.
Through a deeper understanding of India’s historical legacy and contemporary achievements in knowledge, science, and technology, we gain insights into the resilience, creativity, and enduring spirit of innovation that define India’s intellectual heritage.
India’s contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and architecture have not only shaped its own cultural and intellectual landscape but have also influenced global scientific thought and technological progress. The legacy of ancient Indian scientists and scholars continues to inspire contemporary researchers and innovators, reinforcing India’s status as a beacon of knowledge and discovery.
